Combine EKS Support
Combine has support for integrating AWS EKS into an emulated region. However, due to limitations of the AWS EKS architecture, there are a several issues to be aware of when standing up your EKS cluster.
Mention Combine running on EKS here?
Kubernetes Version
Combine enforces which Kubernetes Version are supported in the production environment.
Combine and OIDC
Combine supports EKS OIDC integration without rewriting calls to the OIDC provider — the commercial URL provided by AWS works as-is.
Typically, users employ the WLDEVELOPER role to create the necessary roles. The OIDC provider itself must be created by the government customer on the high side. In Combine, the government customer can be simulated by using the WLCUSTOMER-IT role (or an equivalent outside role).
WLCUSTOMER-IT grants permissions normally reserved for U.S. Government customers, allowing self-service requests and clarifying that it operates outside the Combine emulation boundary.
NOTE that WLCUSTOMER-IT is only for use in simulating actions reserved for the government customer, and not intended for development.
Security Group
Since Combine is proxying traffic from clients to your EKS cluster it must be granted access to the EKS API.
If your Cluster is open to all traffic within the VPC this is not necessary. If not, at a minimum you will need to give the Combine Endpoint Server Security Group access on your Cluster's Security Group.
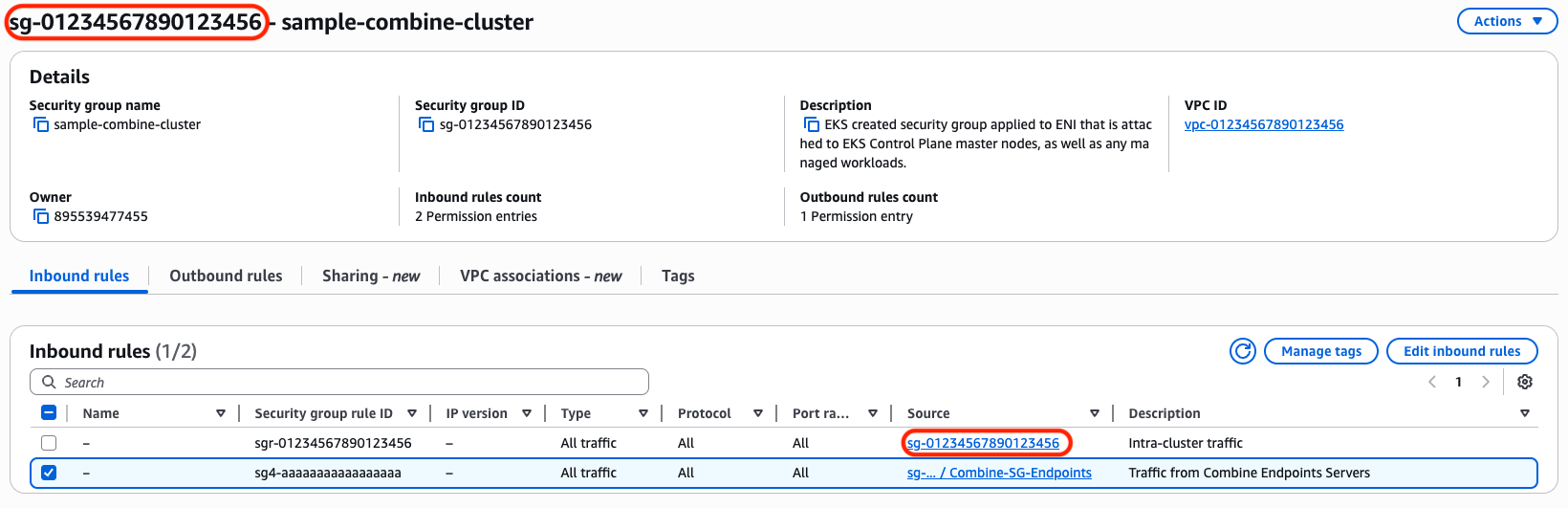
In the screenshot above, note that the 'Source' of the EKS Cluster's Security Group's first rule references itself. You will need to add a rule patterned after the second rule above which references Combine Endpoint Server's Security Group.
Nodes Joining the Cluster
If your nodes are unable to join the cluster, you have several routes to troubleshoot:
- Your Combine Deployment may need the
EnableAirgapAccessEKSon the Combine Policy stack set totrue. This needs to be set for the nodes to communicate with the cluster's API server. The API server lives in AWS's network space, outside of the VPC, so Combine is not able to proxy that traffic over the high side endpoints. - More suggestions forthcoming.
Recommended EBS CSI Driver Configuration
Use a recent EBS CSI Driver version and ensure IMDS is reachable from pods.
Recommended setup:
- Use AWS EBS CSI Driver v1.33+ (newer versions like 1.53 are fine)
- Ensure worker nodes:
- Have IMDS enabled
- Have HTTP PUT response hop limit ≥ 2
- Ensure the CSI controller has credentials via:
- Node IAM role (IMDS), or
- IRSA (if supported and configured)
- Do not assume emulator limitations for IMDS-related errors
With this configuration, dynamic EBS-backed PersistentVolumes can be provisioned successfully in emulated EKS clusters.
PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) stuck in Pending when using the AWS EBS CSI Driver
Most likely, pods cannot reach the EC2 Instance Metadata Service (IMDS), preventing the EBS CSI driver from obtaining credentials. The root cause is usually an incorrect IMDS hop limit.
Detailed answer:
When deploying the AWS EBS CSI Driver in an EKS cluster running inside an emulated region:
- PVCs may remain in
Pendingwith messages like:Waiting for first consumerExternalProvisioning
- Logs may show errors such as:
GetInstanceIdentityDocumenttiming outfailed to refresh cached credentialsno EC2 IMDS role found
The specific misconfiguration in this case would be:
- IMDS HTTP PUT response hop limit set to 1
- Pods require a hop limit of at least 2 to reach IMDS from within the node network namespace
Once the hop limit is increased to 2 on the worker nodes, pods should able to access IMDS, credentials should be retrieved successfully, and PVCs should be bound as expected.
Additional Considerations
- We recommend using IaC (Infrastructure as Code) to provision your EKS Cluster(s). ClickOps has been shown to not be reliably reproducible. There are AWS Console offerings in the AWS and AWS GovClud partitions which are not present in the emulated regions.
- We recommend using version 1.33 or greater of the AWS EBS CSI driver.
- On EC2 instances, including EKS worker nodes, there is a setting on the instance metadata options called
HTTP PUT response hop limit. This controls how many network hops a response from the EC2 Instance Metadata Service (IMDS) is allowed to take..It needs to be set to at least2. More information on the AWS docs here. - Note that Combine does not fully support EKS clusters provisioned with the terraform AWS EKS module version 21.3.1. We anticipate supporting this very soon!
- The Helm Chart for some Plugins may need to be modified, particularly for AWS commercial ARNs, regions, and availability zones.
- Your Combine instance must have Permissions Boundaries and IAM Self Service enabled. If you are not sure if this is enabled on your account, please reach out to a Combine Team member via email.
- You must prefix all roles that do EKS-related work (node groups, pods, clusters) with
PROJECT_as per the customer's high side requirement. Combine will not allow creation of roles that do not follow this format.
Note that EKS add-ons are in experimental support for Combine right now. If you need to use them, please reach out to a Combine team member to discuss your use case.
For a complete working example of how to stand up an EKS cluster within Combine, please see our example repository.